Wave Mechanics:
Schrodinger carried the implication of the wave nature of the electron further and developed a branch of physics called wave mechanics or quantum mechanics.He argued that if De Broglie's concept is correct,it should be able to deduce the properties of an electron system from the properties of an electron system from a mathematical relationship such as wave equation of electromagnetic theory,optics,mechanical vibrations,etc.,
Such a wave equation equation is given by,
\frac{\partial^2&space;}{\partial&space;t^2}=0) -------------------> eqn (1)
-------------------> eqn (1)
where,
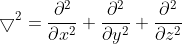
and is the velocity of the wave and the time.
is the velocity of the wave and the time.
The physical meaning of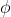 depends upon the problem under consideration. It may be one of the component of electric field,the mechanical displacement,the pressure etc., depending upon the physical problem.
depends upon the problem under consideration. It may be one of the component of electric field,the mechanical displacement,the pressure etc., depending upon the physical problem.
We can eliminate the time variable by assuming a solution in the form,
=\Psi&space;(x,y,z)e^{jwt}) --------------------> eqn(2)
--------------------> eqn(2)
Then equation (1) becomes,
(\Psi&space;)) -------------------> eqn (3)
-------------------> eqn (3)
where,
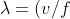)
From De Broglie relationship,
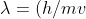=(h/p))
we can write,
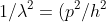=(2m/h^{2})(w-u)) -------------> eqn (4)
-------------> eqn (4)
where kinetic energy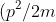) is the difference between the total energy W and the potential energy U.
is the difference between the total energy W and the potential energy U.
Here W = kinetic energy + potential energy which is represented as
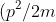=W-U)
=(2m)(W-U))
Substitute eqn (4) in eqn (3),we get the time-dependent
+(8\pi&space;^{2}m/h^{2})(W-U)(\Psi&space;)=0) -------------> eqn (5)
-------------> eqn (5)
The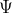 in eqn(5) is called the wave function,it must describe the behaviour of the particle.It is found that the proper interpretation of
in eqn(5) is called the wave function,it must describe the behaviour of the particle.It is found that the proper interpretation of 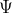 is that it is a quantity whose square the probability gives the probability of finding an electron.
is that it is a quantity whose square the probability gives the probability of finding an electron.
In otherwords, is proportional to the probability that the electron is in the volume dxdydz and the point P(x,y,z) in space.The wave function in above equation describes the behavior of the particle.It is found that the proper interpretation of wave function ,is a quantity whose square gives the probability of finding the electrons.Therefore the wave function must be normalized such that it becomes unity,thus indicating that the probability of finding electron must be unity.
is proportional to the probability that the electron is in the volume dxdydz and the point P(x,y,z) in space.The wave function in above equation describes the behavior of the particle.It is found that the proper interpretation of wave function ,is a quantity whose square gives the probability of finding the electrons.Therefore the wave function must be normalized such that it becomes unity,thus indicating that the probability of finding electron must be unity.
The reason for considering 4A group elements is that these metals in crystalline form can behave as a conductor,semi conductor and insulator.
Such a wave equation equation is given by,
where,
and
The physical meaning of
We can eliminate the time variable by assuming a solution in the form,
Then equation (1) becomes,
where,
From De Broglie relationship,
we can write,
where kinetic energy
Here W = kinetic energy + potential energy which is represented as
Substitute eqn (4) in eqn (3),we get the time-dependent
The
In otherwords,
Limitations of Schrodinger wave equation:
1.Schrodinger equation could be used to find only about the probability that the electron can be found in the neighborhood of a precise point P but could not attempt to locate the particle.
2.The solution of Schrodinger's equation,subject to the proper boundary conditions yields the allowed energies of the particles and its wave function.Therefore it becomes complex to solve higher order functions of wave functions.
Electronic Structure of Elements:
The solution of Schrodinger equation for hydrogen or any multi electron atom need not have radial symmetry.The wave function may be a function of azimuth and polar angles as well as of the radial distance.It turns out that,in general case,four quantum numbers are required to define the wave function.the total energy,orbital momentum,the component of the angular momentum alon a fixed axis in space and the electron spin are quantized.
The four quantum numbers are as follows:
1. The Principal quantum number:
It is an integer 1,2,3,... and determines the total energy associated with a particular state. The number may be considered to define the size of the elliptical orbit,and it corresponds to principal quantum number n of Bohr atom.
2.The orbital angular momentum quantum number :
It takes the values from 0,1,2,3,....,(n-1).This number indicates the shape of classical orbit.
3.The orbital magnetic number:
It may have the values -l,.....,-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4,....l.This number gives the orientation of classical orbit with respect to an applied magnetic field.The magnitude of the component of angular momentum along the direction of the magnetic field is given by m(h/(2)(3.14)).
4.Electron spin:
In order to explain certain spectroscopic and magnetic phenomena, Uhlenbeck and Goudsmith,in 1925,found it necessary to traversing its orbit around the nucleus,the electron must also rotate about its own axis.This intrinsic electronic angular momentum is called electronic spin. when an electron system is subjected to a magnetic field,the spin axis will orient itself either parallel or anti-parallel to the direction of field.The spin is thus quantized to one of the two possible values i.e.,+1/2,-1/2.
Pauli's exclusion principle:
Periodic table of chemical elements may be explained by invoking a law by invoking a law enunciated by Pauli in 1925.He stated that no two electrons in an electronic system can have the same set of four quantum numbers.This statement that no electrons may occupy the same quantum state is known as the Paul exclusion principal.
The inner shell electrons of the atoms are very strongly bound to an atom,and cannot be easily removed.That is,the electron closest to the nucleus are the most tightly bound and have the lowest energy.The atoms for which the electrons exist in closed shells form a very stable configuration.For example,the inert gases He,Ne,A,Kr and Xe,all have either completely filled shells or at least completely filled sub shells.If we consider the elements like carbon,silicon and germanium,each of these elements has completely filled sub shells except for the outermost p shell,which contains only two of the six possible electrons.The reason for considering 4A group elements is that these metals in crystalline form can behave as a conductor,semi conductor and insulator.
This ends the introduction of electronic devices and circuits.
Disclaimer:
I have created this blog for educational purpose,so for that i have written the content by referring many books,web pages.I have also uploaded google images and you tube videos for the better understanding of concept and I would also like to inform you that I am not responsible for the ads which are being posted in my blog.








