Ionization:
The
loosely bounded electrons in an atom generally have more energies, so
these electrons move to stationary states which are farther and farther
away from the nucleus.when the electron have high energy in such a
level that it can completely move out of the field due to influence of
ion and gets detached from it. Then the atom is said to be ionized.The
alkali metals have lowest ionization potentials,where as,inert gases
have the highest values.
Collision of electrons with atom:
In order to excite or ionize an atom,energy must be supplied to it.This energy may be supplied to the atom in various ways.
One of the most important way is through electron impact. other methods of ionization or excitation of atoms are considered below.
One of the most important way is through electron impact. other methods of ionization or excitation of atoms are considered below.
- Suppose that an electron is accelerated by potential applied to the discharge tube.When electron collides with an atom,one of the several effects may occur:
- A slowly moving electron suffers an elastic collision i.e., one entails an energy loss only as required by the laws of conservation of energy and momentum.
- The direction of travel of electron will be altered by collision although its energy remains substantially unchanged.Since this follows the fact that the mass of gas molecule is large compared with that of electrons.
- If the electron possess sufficient energy,the amount depending upon particular gas present,it may be transfer,enough of its energy to the atom to elevate it to one of the higher quantum states.The amount of energy necessary for this process is called excitation or radiation or potential of an atom.
- If the impinging electron possesses a higher energy,say,an amount at least equal to the ionization potential of the gas,it may deliver this energy to an electron of the atom and completely remove if from the parent atom.
Note:
It must not be presumed that incident electron must possesses an energy corresponding exactly to the energy of stationary state in an atom in order to raise the atom into its level. If the bombarding electron has gained more particular state,the amount of energy in excess of that required for excitation,then this excess energy will be retained by incident electron as kinetic energy after the collision or if the process of ionization has taken place,the excess energy divides between the two electrons.
Collision of photons with atoms:
When a photon collide with an atom (say of gas) in excited state, the atom may absorb a photon of frequency V and it may have a transition from lower energy states E1 to higher energy state E2,where,
It should be noted that the atom will not be excited unless the energy of photon corresponds exactly to the energy difference between the two stationary states of the atom.when a photon is absorbed by an atom,the atom is elevated into excited state,the excited atom now returns to its ground state in one jump or in several steps,when a photon is not absorbed by an atom, the atom now returns to the ground state after falling into one or more excitation levels.
The atom exists in several photons corresponding to the energy difference between successive excited levels into which the atom falls.the newly emitted photons have energy less than the energy of impinging photon .so the frequency of emitted photons are different from that of incident photon. If the frequency of impinging photon is high,it may cause ionization of the atom.in this case, the photon vanishes with the appearance of an electron and a positive ion. Here it is not essential that the impinging photon must posses energy exactly equal to the ionization energy of the atom but it must posses energy exactly equal to the ionization energy of the atom but it must posses at least this much energy. When the photon possesses energy exceeding the ionization energy,the excess of energy appears as kinetic energy of emitted electron and positive ion.
Meta stable states:
The atom exists in several photons corresponding to the energy difference between successive excited levels into which the atom falls.the newly emitted photons have energy less than the energy of impinging photon .so the frequency of emitted photons are different from that of incident photon. If the frequency of impinging photon is high,it may cause ionization of the atom.in this case, the photon vanishes with the appearance of an electron and a positive ion. Here it is not essential that the impinging photon must posses energy exactly equal to the ionization energy of the atom but it must posses energy exactly equal to the ionization energy of the atom but it must posses at least this much energy. When the photon possesses energy exceeding the ionization energy,the excess of energy appears as kinetic energy of emitted electron and positive ion.
Meta stable states:
Stationary states may exist by excitation of electron bombardment but not by photo excitation,then the levels that are so formed are called meta stable states.A transition from a meta stable level to normal state with the emission of radiation has a very low probability of taking place.
The long lifetime of the meta stable states arises from the fact that the transition to the normal state with emission of a photon is forbidden.The energy of meta stable state can be expanded so that the atom may return to its normal in two cases:
The long lifetime of the meta stable states arises from the fact that the transition to the normal state with emission of a photon is forbidden.The energy of meta stable state can be expanded so that the atom may return to its normal in two cases:
- When the collision of meta stable atom takes place with another molecule,it gives its energy to other molecule,in the form of kinetic energy of translation or potential energy of excitation.
- When an electron in meta stable state receives additional energy,then the meta stable atom may thereby be elevated to a higher energy state from which a transition to normal level can take place,or else it may be ionized.
If the meta stable atom diffuses to the walls of the discharge tube or to any of the electrodes, therein , either it may liberate its energy in the form of heat or the meta stable atoms might induce secondary
emission.
The wave properties of matter:
When an atom absorb a photon of frequency f and move from the energy level E1 to higher energy level E2 then,
since a photon is absorbed by only one atom,the photon acts as if it were concentrated in one point in space.
According to De-Broglie hypothesis, the dual character of atom i.e., wave and particle nature is not only limited to radiation but also characterized by particles such as electrons, atoms, molecules or macroscopic masses. He has calculated the mass m of the particle traveling with a velocity v when a wavelength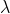 is associated with it. Thus it is given by,
is associated with it. Thus it is given by,
where p is the momentum of the particle.
The existence of such matter waves was demonstrated experimentally by Davinson and Germer in 1927 and 1928 respectively.
We can make use of wave properties of a moving electron to establish Bohr's postulates that a stationary state is determined by the condition that the angular momentum must be an integral multiple of h/2
It seems reasonable to assume that an orbit of radius r will correspond to a stationary pattern.In other words, a stable orbit is an orbit whose circumference is equal to the electronic wavelength.Thus,
Disclaimer:
I have created this blog for educational purpose,so for that i have written the content by referring many books,web pages.I have also uploaded google images and you tube videos for the better understanding of concept and I would also like to inform you that I am not responsible for the ads which are being posted in my blog.



No comments:
Post a Comment